At the beginning stages of a chickenpox infection (1 to 2 days following exposure) a person may begin to feel unwell (malaise) and feverish, develop a headache, as well as experience a loss of appetite. An inflamed rash and fluid-filled blisters typically follow these symptoms.
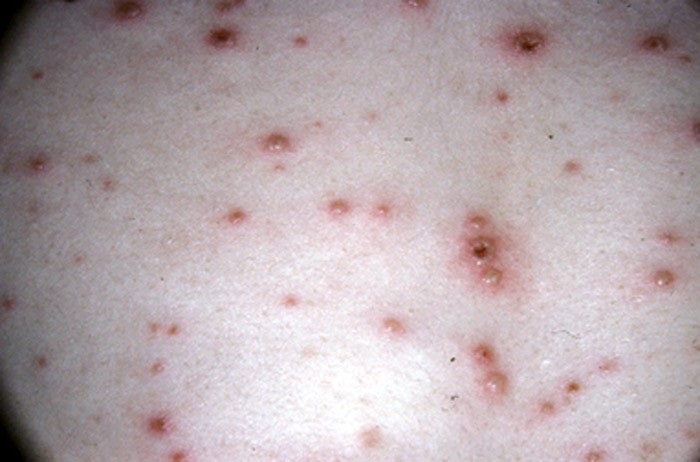
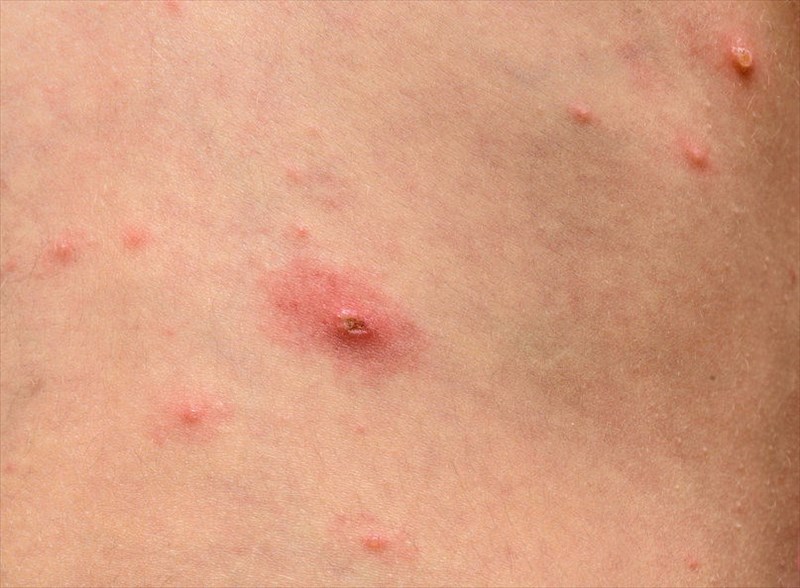
What does chickenpox look like?
The characteristic chickenpox rash and blisters occur in three phases on the body:
- Red or pink-looking bumps (papules), often first noted on the stomach, chest, back or face areas, which then spread throughout the body.
- The bumps fill up with fluid, forming blisters (vesicles), that begin to break open and leak.
- The blisters develop a crust and scab (begin to heal).
Not every blister on the body will form at the same time following exposure to the virus, but these will follow the same phase pattern. New blisters will develop throughout the infectious period (time when the virus is prone to spreading). This is why a person remains contagious for several weeks, until all bumps have scabbed over and begun to heal.
All symptoms are typically mild for young children. Those who have been vaccinated (including children and adults) can also still get an infection, but symptoms will be milder and produce fewer blisters on the body. A severe case of chickenpox can result in rash and blisters spreading throughout the body. In some instances, small lesions may even form on the throat, around the eyes and in the mucus membranes of the urethra, vagina or anus.
If you suspect a case of chickenpox, it is best to get in contact with your doctor as soon as possible and notify them of your suspicion before arriving for a consultation.
If you note that a rash appears to have spread to one or both eyes, is very red, tender or warm, or is accompanied by symptoms of disorientation, dizziness, shortness of breath, a rapid heartbeat, a cough (which worsens), poor muscle coordination, a stiff neck, a very high fever or vomiting, it is best to see a medical professional as soon as possible. Any of the aforementioned symptoms could indicate another possible medical condition or complication which may require prompt medical intervention.
Other serious warning signs for immediate medical attention include:
- Confusion
- Difficulty walking or waking up
- Other breathing difficulties
- Severe abdominal pain
- A haemorrhagic rash (signs of bruising or bleeding along with a rash)