Strep throat is not a life-threatening infection, but it can lead to other health complications if not effectively treated. Severity of an infection varies from one person to the next. The primary symptom of a sore or painful throat may or may not be accompanied by other signs of infection.
Normally symptoms of strep throat will develop within 2 to 5 days following exposure to the bacteria (this is known as the incubation period). An infection can clear on its own without treatment (typically within 3 to 7 days).
The most common symptoms of strep throat are:
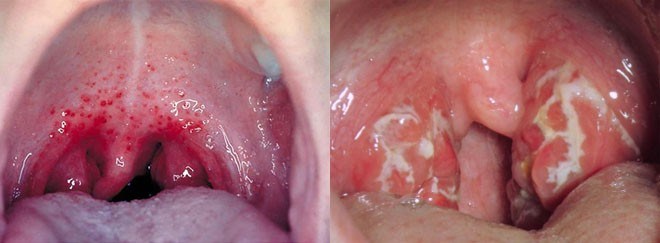
- Tenderness / soreness in the throat (with red and white patches or streaks of pus, and swollen tonsils – this can lead to bad breath)
- Small red, white or yellow spots at the back of the mouth (near the roof of the mouth, or on the soft or hard palate)
- Fever (sudden and often around 101˚F or 38˚C or higher)
- Chills and / or body aches
- Swollen lymph nodes (on the sides of the upper portion of the neck)
- Difficulties with swallowing / pain when swallowing
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Rash (which can spread to the neck or chest, and eventually the entire body) *this is normally associated with scarlet fever
- Nausea and / or vomiting
- Dehydration (due to a lack of fluid intake) – in varying degrees
- General malaise (feeling unwell)
A person infected with strep throat may be contagious for between 2 and 3 weeks even if symptoms have cleared. Taking antibiotics can reduce this within 24 hours of the first dose, as well as help to prevent the infection from worsening.
How symptoms of strep throat can affect different age groups
- Infants: Infection in young babies is not common. When an infection does occur, babies typically are reluctant to feed and display bouts of irritability and fussiness. A baby may also experience a nasal discharge and low-grade fever.
- Young children: Along with a sore throat and pain when swallowing, young children may also experience loss of appetite and abdominal pain.
- Older children and adolescents: As children grow older, strep throat infections can become more uncomfortable. Throat pain is often severe, and accompanied by a high fever (typical of a bacterial infection).
- Adults: Symptoms are generally mild, but can be severe in some cases.
How to tell the difference between tonsillitis and strep throat
Tonsillitis is generally caused by both viral and bacterial infections. Viruses which can cause tonsillitis as a symptom include influenza (flu), herpes-simplex virus, HIV, coronavirus, Epstein-Barr virus or adenovirus.
The most common bacteria to cause tonsillitis is the same group A Streptococcus which results in strep throat. Other species of strep bacteria, such as chlamydia pneumoniae (chlamydia), Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonorrhoea) and staphylococcus aureus can also lead to the development of tonsillitis. Strep throat, however, is not caused by any other group of bacteria.
The two conditions may display similar symptoms. Symptoms of tonsillitis other than those similar to strep throat include:
- High fever (higher than in the case of strep throat -102.6°F or 39.2°C, or higher)
- Stiff neck
- Upset stomach
- Discolouration on or around the tonsils (white or yellow)
When to call the doctor if you suspect a strep throat infection
When a sore throat …
- Lingers for 2 days (48 hours) or more
- Is accompanied by white patches or streaks on the back of the throat
- Is accompanied by dark or red spots on the palate of the mouth or tonsils
- Is accompanied by a pink rash on the skin that feels like fine sandpaper
- Is accompanied by a high fever lasting longer than 2 days (48 hours)
- Results in difficulties with swallowing
- Has not shown improvement within 48 hours of being diagnosed and treated with antibiotics
If a strep throat infection has been diagnosed and treated, and symptoms don’t appear to clear within 1 to 2 weeks, a doctor may wish to check for signs of rheumatic fever. Symptoms associated with this condition include body weakness, joint pain, a raised red rash, lumps beneath the skin, shortness of breath and uncontrolled jerking movements (the limbs).
If a sore throat is ever accompanied by the below symptoms, immediate medical care is required:
- Difficulties with breathing (with or without audible noises)
- Inability to swallow any amount of food and liquids, or saliva
- Inability to open the mouth
- Throat pain which is severe and accompanied by swelling or redness around the neck area
- Bleeding in the throat
When a sore throat is not likely strep throat
The general rule of thumb is that the more cold-like symptoms are present, such as a congested nose, sneezing or coughing, the more likely it is that a sore throat is as a result of a viral infection (not a bacterial one).
Any instance of a sore throat that is accompanied by a high fever and swollen lymph nodes should be checked by a medical doctor. Tests may be required to make an accurate diagnosis of the type of infection present.