- Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
- What causes hand, foot and mouth disease?
- What are the symptoms of hand, foot and mouth disease?
- What are the complications and risk factors of hand, foot and mouth disease?
- Diagnosis, treatment and outlook for hand, foot and mouth disease
- FAQ about hand, foot and mouth disease
What is hand, foot and mouth disease?
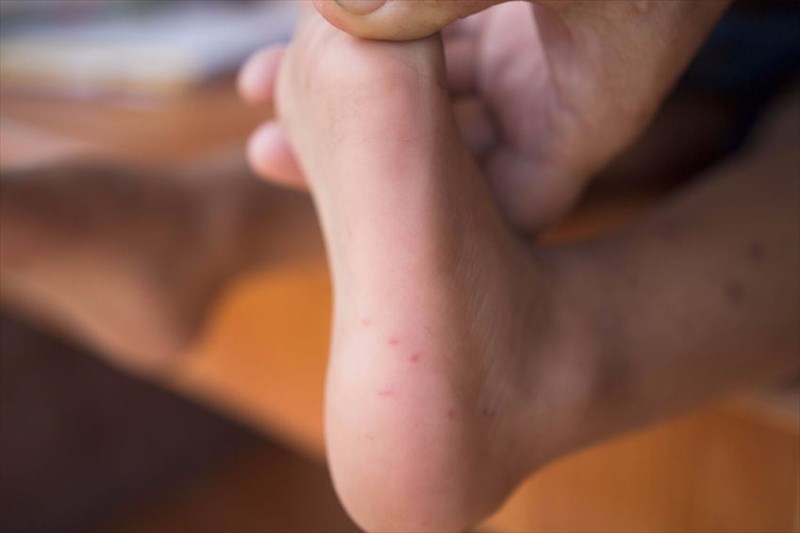
Hand, foot, and mouth disease, also known as HFMD, is a highly contagious yet mild viral infection that commonly affects infants and children, but may also occur in adults. It is characterised by sores (small red bumps or blisters) developing on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet and occasionally the buttocks or genitals. A related infection, known as herpangina may result in sores developing on the inside of the mouth which make chewing and swallowing painful.
The illness occurs due to infection with one of the non-polio enteroviruses, with coxsackievirus A type 16 being the most common cause.
There is no specific treatment for this virus, but the risk of contracting it can be reduced through sound hygiene practices and educating children on how to wash their hands properly.
**MyMed Memo: It is important to note that hand, foot, and mouth disease should not be confused with foot and mouth, or hoof and mouth disease which is caused by a different virus and affects sheep, cattle and swine.
Other Articles of Interest
Rotavirus
Rotavirus is one of several viruses known to affect the intestinal tract causing gastroenteritis and diarrhoea. It can be treated easily. Here's what you need to know...

Diarrhoea
Suffering from a runny tummy? Having diarrhoea can often be an embarrassing and even painful experience. Find out all you need to know about dealing with and combating this condition.

Meningitis
Any condition that directly affects the brain and spinal cord can ignite intense fear and anxiety in anyone. Meningitis infections should always be taken seriously. Learn more here...
