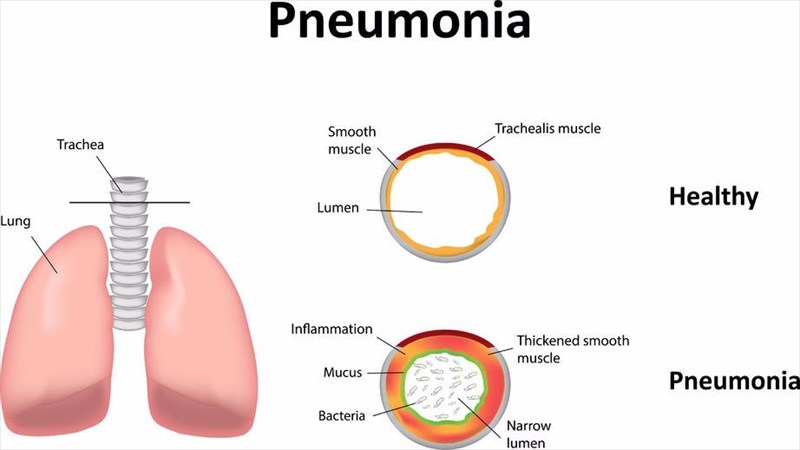
What causes pneumonia?
Pneumonia is caused by viruses, and bacteria, and in some cases a fungus or parasite. Pneumonia is however, very rarely brought on by a parasite or other organism. In the vast majority of cases, the bacteria or virus causing the infection is identified as streptococcus pneumoniae.
Pneumonia can also be caused by a bacteria-like organism called mycoplasma pneumoniae. Mycoplasma pneumonia is also known as “walking pneumonia” or atypical pneumonia with milder symptoms. A common form of pneumonia, especially among people under the age of 40, symptoms are easily treated with antibiotics.
The flu virus, RSV (respiratory syncytial virus) and the human Rhinovirus can also cause pneumonia. RSV is a common viral infection experienced in childhood. Symptoms experienced include a runny nose, coughing and wheezing, and tends to clear easily with home care.
Sometimes RSV can worsen and develop into pneumonia or other breathing difficulties such as bronchitis, which will require medical treatment and / or hospital care.
Those with impaired or weaker immune systems are at higher risk of pneumonia. Some types of fungi, such as Pneumocystis jiroveci (previously known as Pneumocystis carinii or PCP) have been known to cause pneumonia in people diagnosed with HIV / AIDS and tuberculosis. Some doctors may recommend an HIV test if it is suspected that Pneumocystis jiroveci is the cause of a pneumonia infection as this can often be one of the first signs of the disease.
Types of pneumonia
The most common types of pneumonia are:
- Bacterial: This type of pneumonia affects anyone and at any age. The infection develops either on its own or following a round of serious cold or flu. Bacteria that most cmmonly causes the infection is streptococcus pneumoniae. Other known bacteria that cause pneumonia are Haemophilus pneumoniae and Moraxella catarrhalis. Chlamydophila pneumonia or legionella pneumophila (which causes Legionnaire's disease, a serious form of pneumonia) are atypical causes.
- Viral: Respiratory viruses are often the cause of an infection, especially among seniors and young children. In many cases, pneumonia is not severe and lasts a short time. A severe case of the flu that develops into pneumonia may, however, cause viral pneumonia which can be severe and even life-threatening. Viral pneumonia is particularly harmful to pregnant women and those with heart and lung conditions.
- Mycoplasma: These organisms are not classified as viruses or bacteria, although they have traits common to both. Mycoplasmas generally cause milder cases of pneumonia and are the smallest agents of the condition affecting human beings. As a cause, mycoplasmasare most common among older children and young adults.
