What are the causes of frequent urination?
Common causes
- Drinking too many liquids – If you are drinking more fluids than your body requires, this can lead to the need to urinate more frequently.
- Caffeine, artificial sweeteners, smoking, alcohol and some foods –
- Tea and coffee – The main ingredient in coffee and black tea is caffeine. This may increase your bladder activity as caffeine acts as a natural diuretic.
- Carbonated beverages – The bubbles or fizz in carbonated drinks can aggravate your bladder. The combination of the fizz and caffeine found in these drinks can lead to frequent urination.
- Chocolate – Many people are unaware of this, but chocolate also contains small amounts of caffeine although the impact on your urination is not always obvious. However, consuming a large amount of chocolate may be a contributing factor to frequent urination.
- Sweeteners – Some research suggests that both natural and artificial sweeteners may aggravate your bladder as sweeteners have been linked to cystitis (i.e. a condition that causes pressure and pain in the bladder)2.
- Smoking – Chronic coughing which is linked to smokers may induce urinary incontinence problems as extra pressure is put on the muscles in the bladder.
- Alcoholic beverages – Alcohol is also a diuretic, may irritate your bladder and even disrupt the messages to the brain making you feel as though you need to urinate more frequently
- Tomato products – Tomatoes are acidic foods that can potentially irritate your bladder lining.
- Spicy foods – Foods that cause your lips to burn or your eyes to water may also irritate your bladder due to their spice content.
- Oranges, lemons and limes – Citrus fruits contain large amounts of citric acid, this can worsen bladder control if the lining of your bladder becomes agitated by it.
**My Med Memo – Everyone reacts differently to different food and drinks, it is therefore advised that you make a point of remembering which foods and beverages aggravate your bladder.
Medical causes
The commonly seen medical causes of frequent urination include the below-mentioned conditions:
- UTI (urinary tract infection) – A UTI, is a very common infection among men and women (particularly women) and refers to an infection of any area of the urinary system such as the urethra (this is the tube responsible for carrying urine from the bladder, out of the body), kidneys or bladder. A UTI can be an uncomfortable and even painful condition but tends to pass within a few days and is easily treated through the administration of antibiotics.
An infection of the bladder only is also known as cystitis and is caused by a type of bacteria known as Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is found in the GI (gastrointestinal tract), however, other forms of bacteria may also cause the infection. It is also possible for sexual intercourse to result in cystitis. Women in particular, are at risk of infection due to their unique anatomy and the short distance between the urethra and anus, as well as the urethral opening to their bladder. During sexual intercourse, the urethra is exposed to bacteria occurring in the genitals and anus, which may then enter the urethra, bladder and kidneys, causing an infection.
An infection of only the urethra is known as urethritis, this type of UTI occurs when gastrointestinal bacteria enter the urethra from the anus. Due to the female urethra being situated in close relation to the vagina, it is possible for sexually transmitted diseases/infections (STIs/STDs) such as chlamydia, herpes, mycoplasma and gonorrhoea to result in urethritis.
A UTI results in inflammation of the wall of the bladder which may result in the urge to empty the bladder more frequently (i.e. frequent urination).
- Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome) – This is a condition characterised by pain in the bladder and pelvic region. This disorder is often confused with a urinary tract infection, however, there is no infection present and the exact cause of the condition is unknown. The symptoms include chronic pressure, discomfort, tenderness and/or pain felt in the bladder, pelvic area and lower abdomen. If you have this condition, you will often feel an urgency to urinate without warning and urinate more than the average amount (four to seven times a day)3. You may also experience pain when your bladder begins to fill, this pain will worsen until urination occurs.
- Diabetes – Also known as diabetes mellitus, diabetes is one of the most common causes of frequent urination, which, in this case is known as polyuria. Polyuria is a result of excessive fluid intake due to excessive thirst or polydipsia (also a symptom of diabetes). If you are diabetic, your blood sugar levels will abnormally high and not all of the sugar will be readily absorbed by the body. As such, high amounts of blood glucose accumulate in your kidney tubules, resulting in the body needing to rid itself of unused glucose (sugar) which it does through the production of urine. Chronically high blood sugar may also damage the nerves controlling the bladder, compounding frequent urination and making bladder control difficult.
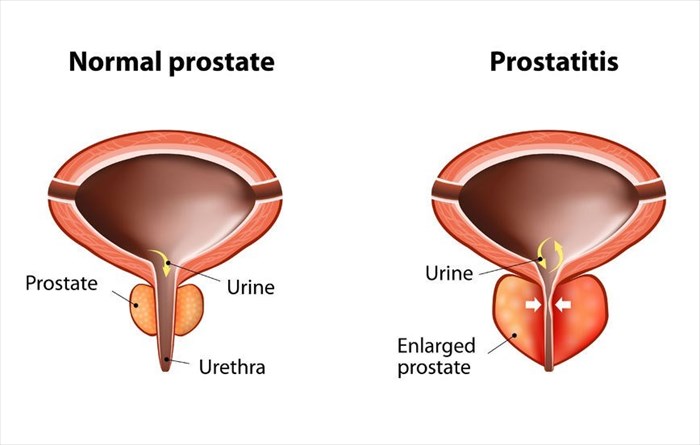
- Prostate issues – Prostate issues such as an enlarged prostate, can cause the prostate to place extra pressure on the urethra by pressing against it. This action may agitate the bladder walls, causing them to contract even if there is only a small amount of urine present, the result of this contraction is often frequent urination.
- Pregnancy– If you are pregnant, then your growing uterus will place pressure on your bladder, resulting in one of the most common symptoms of pregnancy… frequent urination. This can occur as early as the first few weeks of pregnancy.
In addition to this, hormonal changes will also contribute to the need to urinate more than normal. When you are pregnant, your body produces more blood to accommodate for the developing foetus, this extra blood flow results in the kidneys producing more urine which will peak aroundweeks nine to 16 of pregnancy, and begin to settle down thereafter. It is advised that you do not attempt to restrict your fluid intake to try and control frequent urination during pregnancy. It is vital that you keep yourself and your growing baby hydrated. Frequent urination is to be expected as a natural and healthy part of pregnancy and resolves thereafter. - Neurological conditions – Suffering from a stroke (i.e. the sudden death of brain cells as a result of a lack of oxygen, rupture of an artery supplying the brain or a blockage of blood flow) or other neurological diseases can result in damage to the nerves supplying information to the bladder. Damage such as this may lead to issues with the functioning of the bladder such as a sudden urge to urinate and frequent urination due to misinformation supplied by the brain to the bladder, activating the void reflex unnecessarily.
- Use of diuretics – A diuretic is a substance or medication that promotes the increased production of urine in order to rid the body of excess water. These are often used to ease swelling and the symptoms of water retention in the body. Diuretics are also known as ‘water pills’ and some of these forms of medication used in the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure) flush out excess fluid in the kidneys, resulting in frequent urination.
- Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) – The hallmark symptom of overactive bladder syndrome is urinary urgency that is often associated with nocturia and urinary frequency. If you suffer from an OAB then you may also experience urge incontinence, this refers to the intense need to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine.
The symptoms of this condition are primarily caused by the involuntary contractions of the smooth muscle found within the bladder wall (known as the detrusor muscle). This muscle relaxes in order for urine to fill and be stored in the bladder and contracts in order for it to be released during urination.
Recurring involuntary contractions are referred to as detrusor overactivity. The cause of this is often due to some of the conditions mentioned above such as diabetes, neurological disorders, UTIs, or tumours, bladder stones and even excess consumption of alcohol or caffeine.
References:
2. Medicine Plus. Cystitis – non-infectious. Available: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/interstitial-cystitis-painful-bladder-syndrome/symptoms-causes [Accessed 15.02.2018]
3. Medicine Plus. 2017. Symptoms & Causes of Interstitial Cystitis. Available: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000514.htm [Accessed 13.12.2017]