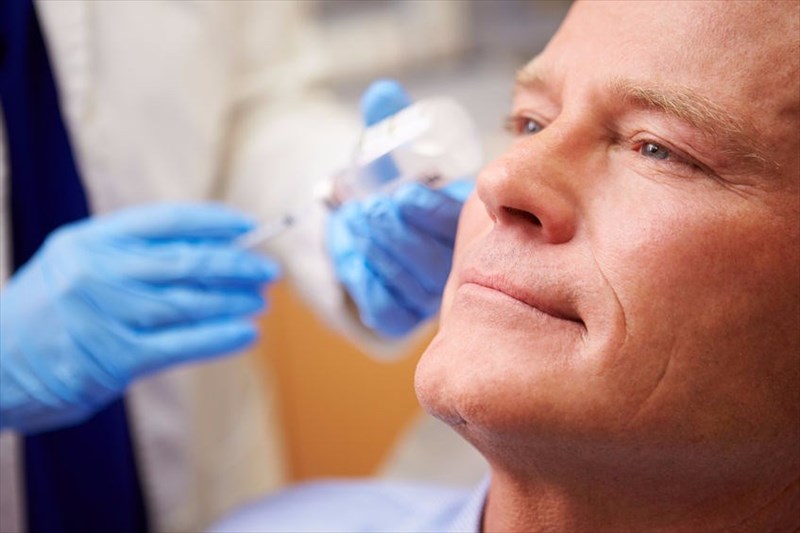
- Botox
- How did Botox begin?
- How is Botox administered and what wrinkles does Botox treat?
- How long does a Botox injection last?
- The sites on the body where Botox will work best
- Candidates for Botox
- Side effects and complications of Botox
- Medical and cosmetic uses of Botox
- Some questions about Botox answered
Clostridium botulinum, is a bacterial organism that produces Botox, it is found in its inactive form in natural settings such as forests and cultivated soils as well as in the sediment of streams, lakes and coastal waters. The bacterium is also found in the tracts of fish, mammals and in the viscera and gills of shellfish.
These naturally occurring forms of the bacterium are typically harmless, the problem arises when the spores convert into vegetative cells, which results in the cell population increasing. This is when the bacterium produces the botulinum toxin, which is a deadly neurotoxin that can result in botulism (an infection with the toxin). It is interesting to think that such a dangerous toxin, which is injected into the human body in a weakened state, is found in the natural environment in a dormant state.
Neurotoxins work by targeting and disrupting the nervous system (the word ‘neuro’ relating to nerves). The nervous system is a network made up of nerve cells that transmit impulses between different parts of the body, it is basically the message system of the body which is constantly communicating. A neurotoxin is able to block this system, causing the neurons (nerve cells - the messengers) to not work as effectively.
To think about it in a simple way, when this toxin enters the body, it blocks the signal between the messenger cells, which can be likened to the cutting of telephone lines, which stops the messages from being sent to other parts of the body.
The neurotoxin that produces Botox can be divided into eight different types, these being, A, B, C [C1, C2], D, E, F, G 18 and H.19. The types A, B, E and in rare occasions, F, are known to cause botulism in humans. Types C and D are known to cause illnesses in some birds, fish and other mammals. Type A is typically used for cosmetic procedures.
Botox was first discovered in the 1820s by the German scientist Dr Kerner. At the time, he was trying to understand what caused food poisoning and found that it was a specific toxin in spoiled sausages. Over 70 years later, in wanting to further explore the properties of the toxin, another doctor then expanded on this discovery and found several strains of the botulinum toxin, four of which were harmful to humans.
It was only in the 1960s that scientists found that injecting small doses of the toxin type A seemed to relax hyperactive muscles, it was then used for several years to treat muscle spasms. It was first used to treat strabismus (squint). Further research also began in exploring the helpful effects of the toxin. In the 1980s, the botulinum toxin was called Botox and was then FDA approved for treatment on humans as an aesthetic treatment in 2002.
