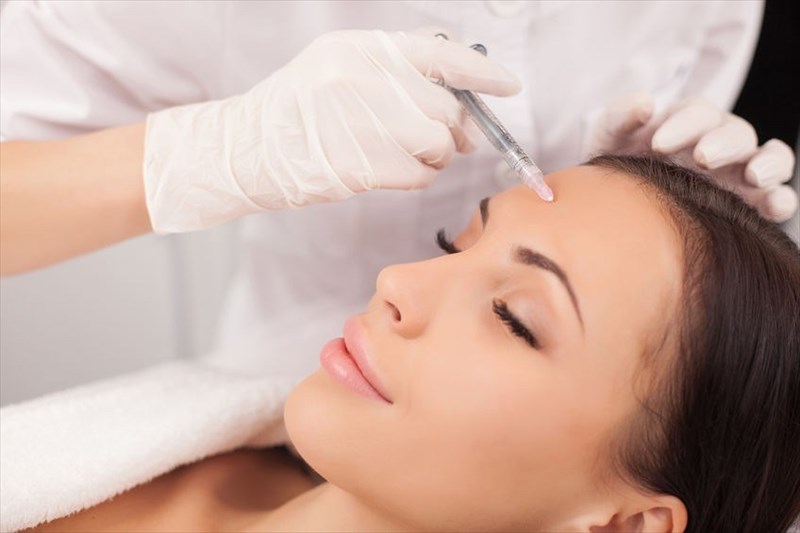
- Botox
- How did Botox begin?
- How is Botox administered and what wrinkles does Botox treat?
- How long does a Botox injection last?
- The sites on the body where Botox will work best
- Candidates for Botox
- Side effects and complications of Botox
- Medical and cosmetic uses of Botox
- Some questions about Botox answered
What is Botox?
Botox, the miracle treatment for wrinkles and the reason why so many modern men and women seem to defy aging. In this day and age, it is hard to tell how old anyone actually is due to these types of aesthetic procedures.
What many people don’t know, is that Botox is actually a toxin. In modern medicine, it is used to treat specific muscular conditions and cosmetically in aesthetic medicine to smooth out wrinkles. In being a neurotoxin, it works by temporarily paralysing the muscles. The Botulinum type A toxin is marketed under the brands names Botox, Xeomin and Dysport, with Botox being the first brand to market.
Botox is derived from a neurotoxin that is produced by Clostridium botulinum, a bacterium also known as botulinum toxin, this toxin is an organism that is found in the natural environment in an inactive and non-toxic state. Scientists discovered a way to use this toxin for human advantage though using small and diluted amounts that are directly injected into the muscles, causing them to weaken.
It is the most popular kind of cosmetic treatment with a staggering six million Botox treatments administered every year. The most common use of Botox is to smooth out wrinkles such as crow’s feet, forehead and frown lines, drastically reducing the effects of aging. However, it can also be used medically to prevent excessive sweating, migraines, some bladder, bowel and muscular disorders. It becomes easy to understand why the drug is sometimes referred to as the ‘miracle poison’.
**Interesting fact, botulism, is an infection with the botulinum toxin which can lead to respiratory failure and even death. A mere gram of the toxin is able to kill over one million people and two kilograms is able to kill the entirety of the human population. However, the toxin used in Botox is purified and mostly harmless.
Many people do not know the severity of the toxin as the use of it has been socially accepted for years and FDA approved since 2002. The following article outlines the important factors of Botox, what it does, how it is administered and most importantly, what it is made of, drawing focus to the cosmetic uses of Botox and then touching on the medical side of it. It must be noted that this information is written only to serve as a guideline to help you make better informed decisions about whether or not this procedure could be for you and is not intended as a diagnosis or professional medical opinion. Please consult with your doctor for that.
How does Botox work?
As mentioned, being a neurotoxin, Botox blocks the signals sent from the nerves to the muscles. For cosmetic use, the facial muscles injected with Botox are unable to contract which results in the wrinkles in the overlying skin, relaxing and softening in two weeks.
Being injected in extremely small doses, the muscles are left without the instructions from the neurons to contract and are then left paralysed. To be more scientific about this process, the chemical messenger released by the nerves that causes the muscles to contract is called acetylcholine (ACh), which is a neurotransmitter. When Botox is injected, it blocks the release of this neurotransmitter which stops the contraction of the target muscles. The effect of the toxin results in abnormal muscle contraction being reduced, allowing the muscles to become less stiff.
Other Articles of Interest

Headaches
Headaches. We all get them. When is a headache something to worry about? What are the different type and how should a headache be best treated? We take a look at the various common types and causes...
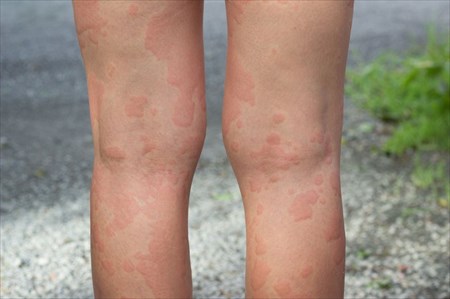
Hives (Urticaria)
Hives are characterised as clusters of swollen, raised welts on the surface of the skin. What causes them? Are there different types? And how should you go about treating them?

Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that gradually causes a degeneration of the brain's nerve cells responsible for the control and regulation of body movements.
