
Causes and risk factors
Exact causes of the malfunction that occurs in the body is not specifically known, but is largely attributed to both genetic and environmental factors. These include:
- A lack of insulin production (Type 1 diabetes)
- Insulin resistance (Type 2 diabetes)
- Pregnancy (Gestational diabetes)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome / PCOS (A condition where a woman experiences irregular menstrual periods, excess hair growth and obesity.)
- Genetics and family history (Odds do appear to increase if a parent or sibling has diabetes)
- Age (The risk of type 2 diabetes does appear to increase as a person ages, particularly after 45. Younger adults or children with decreased muscle mass and reduced amounts of exercise are also at risk. Typically type 1 diabetes is diagnosed before age 30).
- Obesity (Excess body fat causes inflammation and leads to insulin resistance. Not all obese or overweight individuals develop diabetes. The link between the two is still be researched).
- Poor diet (An increased resistance to insulin occurs in diets high in calories, fat and cholesterol)
- Lack of exercise (Regular aerobic exercise and resistance training help muscle tissue respond better to insulin)
- Ethnicity (Some ethnic groups have been noted to have a higher diagnosis rate of diabetes – although research is not 100% conclusive. These include African-Americans, Native Americans, Hispanic/Latino-Americans, Asians, Alaska Natives, Pacific Islanders and people of Indian origin.
- Exposure to a viral illness (This can play a role in type 1 diabetes)
- Abnormal cholesterol and triglyceride levels (i.e. fat carried in the blood. Low levels of high-density lipoprotein / ‘good cholesterol’, increases the risk for type 2 diabetes)
- The presence of autoantibodies (Damaging immune system cells)
- High blood pressure (More than 140/90 millimetres of mercury is linked to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes)
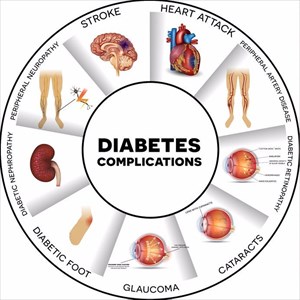
Diabetes complications and health concerns
Long-term health concerns because of diabetes lead to a higher risk of other complications. The less your blood-sugar is controlled, the higher the risk of other health problems, many of which are disabling or even life-threatening.
These include:
Heart problems and cardiovascular disease
- Neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Nephropathy (kidney damage)
- Retinopathy (eye damage)
- Skin infections (bacterial and fungal)
- Hearing impairment
- Alzheimer’s disease
Gestational diabetes complications for a baby include excess growth, low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), type 2 diabetes in later life stages and even death (before or shortly after birth). A mother can experience complications such as preeclampsia, needing a caesarean due to the large size of the baby, damage to the heart, kidneys, nerves and the eye, as well as subsequent gestational diabetes in another pregnancy.

 Heart problems and cardiovascular disease
Heart problems and cardiovascular disease