What is gonorrhoea / gonorrhea
Gonorrhoea (also spelled 'Gonorrhea') is a contagious infection with the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae that typically occurs in warm, clammy areas of the body. A sexually transmitted disease (STD), gonorrhoea is passed from person to person, mostly through unprotected, oral, anal or vaginal sex.
Areas of the body this STD commonly infects include the urethra in males (the urethra is a tube that empties urine from the urinary bladder), vagina, anus, female reproductive tract (uterus, the fallopian tubes and cervix), eyes and throat.
Those at risk of infection are individuals with multiple sexual partners, or those who don’t use protection (a condom) when having sex. Abstinence, monogamy (sex with only one partner), and proper condom usage are some of the best means of protection or prevention. Behaviours like substance abuse (drugs and alcohol), can also make a person more vulnerable to engaging in unprotected sex, and thereby at higher risk of an STD infection.
Gonorrhea, also known as ‘the clap’ or ‘the drip,’ can also be transmitted through infected bodily fluids from mother to child (especially during childbirth). A baby with the infection commonly experiences complications with one or both eyes.
This STD affects both men and women, but in many cases, shows no symptoms of infection or illness. It is not uncommon for some infections to go completely unnoticed for a period of time. Gonorrhea infections are diagnosed with an STD test and must be treated by a medical doctor as soon as possible.
Other Articles of Interest
STD testing and at home STD test options
Think you may have an STD? Learn more about how to find out privately here.

Vaginal discharge in adult women
Suffering from abnormal vaginal discharge and not sure why? Find out here.
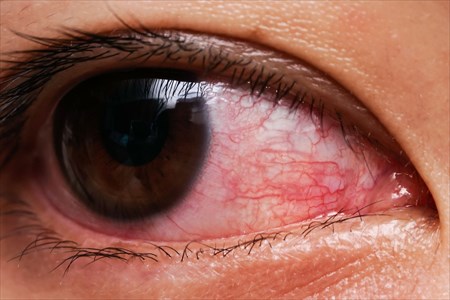
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
Did you know that gonorrhea can cause conjunctivitis (pink eye)? Learn more here.
