- Gum disease (Periodontitis)
- What is the difference between periodontitis and gingivitis?
- What are the stages of periodontitis?
- What are the symptoms of periodontitis?
- What are the different types of periodontitis?
- What are the causes, risk factors and prevention for periodontitis?
- How is periodontitis diagnosed and treated?
- FAQ regarding gum disease
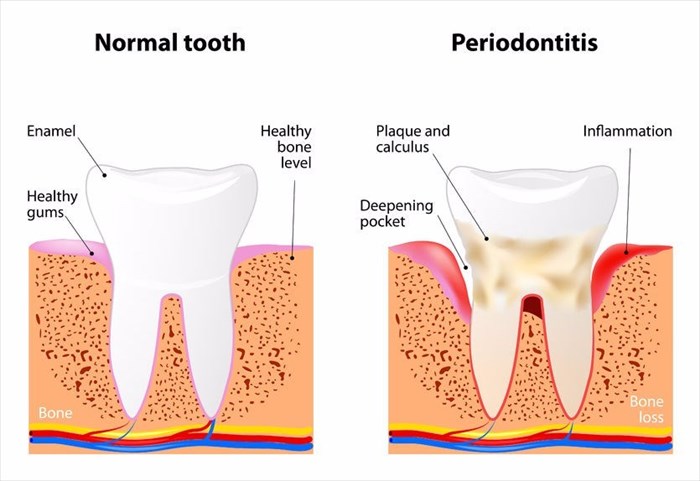
What is gum disease (periodontitis)?
Periodontitis, pronounced “per-e-o-don-TIE-tis”, is a severe form of gum disease and involves periodontal infection that causes damage to the soft tissue of the gums, which may lead to the destruction of the supporting bone of your teeth. This infection can result in the loosening of the teeth and may ultimately lead to tooth loss.
Periodontitis is a common but preventable condition as it is generally caused by neglecting your oral hygiene. Your risk factors for developing periodontitis will be significantly decreased through brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing once a day and attending regular, bi-annual check-ups and professional teeth cleanings with your dentist and oral hygienist.
There are different types of gum disease, gingivitis and periodontitis being the most commonly seen infections. Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums that if left untreated, can progress, leading to periodontitis. The information in the navigation menu above will focus on periodontitis, however, for your own understanding, the section that follows further explains the difference between gingivitis and periodontitis.
Other Articles of Interest

Stress
Stress can affect everyone differently. It is your body's biological response to a certain situation. It is important to know how to deal with stress in order to develop certain coping mechanisms...
X-rays
X-rays are a very common procedure that many of us have had to have or may have in the future. If you want to know more about the imaging test, read all about it here.

The facts on steroids for muscle building
An objective view of the side effects, uses and types of popular anabolic steroids and the impact they are having on the fitness industry.