- Liver Disease / Hepatic Disease
- What are the causes/types of liver disease?
- What are the stages of liver disease from initial inflammation to liver failure?
- What are the symptoms and risk factors of liver disease?
- What is the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of liver disease?
- The liver disease diet and outlook
What are the causes/types of liver disease?
Infection
Viruses and parasites can infect the liver which results in the reduction of liver function as a result of the inflammation caused by the infection. The viruses causing damage to the liver can spread through semen, blood, contaminated water or food, or coming into close contact with an infected person. Hepatitis viruses, which cause inflammation of the liver, are the most common form of liver infections.
These infections include:
- Hepatitis A – This infection is a result of the hepatitis A virus. Patients usually contract this infection through the consumption of contaminated food and drinks. The items are often contaminated by an infected person’s faeces. This infection is common in places where there is poor sanitation and hygiene practice. The virus infects the liver and causes symptoms that are flu-like as well as jaundice (often evident by the yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes).
- Hepatitis B - This infection is a result of the hepatitis B virus and is spread within the infected person’s blood. This infection is commonly seen worldwide, usually spreading from an infected woman to her baby in the womb (in utero transmission), through the sharing of needles, sexual contact or accidentally coming into contact with infected blood. The virus is transmitted via blood, saliva, semen and other bodily fluids. The symptoms are typically the yellowing of the person’s eyes, dark urine and abdominal pain. Most cases disappear on their own whereas the more severe cases can result in liver tissue scarring and may even require a liver transplant.
- Hepatitis C – This infection is a result of the hepatitis C virus and is spread through contact with contaminated blood. The majority of patients do not have any symptoms, if symptoms do develop they may include nausea, fatigue, loss of appetite and jaundice.
Abnormalities of the immune system
Autoimmune diseases, conditions where the immune system mistakenly recognises the body’s healthy cells as invaders and attacks them, are disorders that can have an effect on the liver. Some examples of these diseases include the following:
- AIH (Autoimmune hepatitis) – This is a chronic disease of which the exact cause is still unknown. This condition involves the immune system attacking the liver directly and can eventually lead to cirrhosis which can progress causing liver failure.
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis – This condition was formerly known as PBC (Primary biliary cirrhosis) and is a disease that progressively destroys the bile ducts which become inflamed and collapse as the disease takes its course. The inflammation of the bile ducts causes scarring which will narrow the ducts resulting in damage to the liver and
Genetics
Gene mutations that are inherited from parents can result in the build-up of a number of substances in the liver, this will eventually lead to liver damage. Liver diseases that are genetic include:
- Hemochromatosis – This is a condition that causes an overload of iron in the body. This excess amount of iron can be toxic to the organs and can even lead to various conditions such as an irregular heartbeat, cancer and severe liver damage (cirrhosis).
- Primary hyperoxaluria with oxalosis – Hyperoxaluria is condition also referred to as Bird’s disease after the first person to describe it. The disease occurs when the levels of oxalate in the urine are too high. Oxalate is one of the body’s natural chemicals that is also found in some kinds of food. In this type of hyperoxaluria, being primary hyperoxaluria, the liver does not create enough of the enzyme needed to break down the oxalate levels. When oxalate combines with calcium, creating kidney stones, this can result in renal failure (kidney failure), which is known as oxalosis. In oxalosis, the oxalate forms crystals which start to build-up in a number of organs, causing damage and inflammation.
- Wilson's disease – This is a rare condition that is inherited and results in excessive amounts of copper accumulating in the brain, liver and a number of other important organs.
Growths and cancer
Some examples of growths and cancer that can lead to liver disease are:
- Bile duct cancer
- Liver cancer
- Liver cell adenomas – also known as hepatic adenomas or hepatocellular adenomas, these are tumours on the liver that are benign (non-cancerous) and may result in haemorrhaging of the liver.
Other liver disease causes
Some additional and common liver disease causes may include:
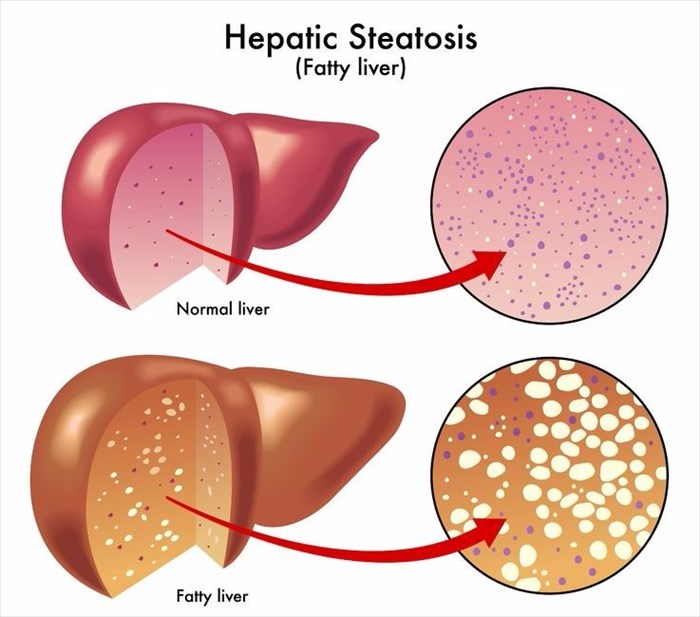
- NAFLD (Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) – Simply put, this is the accumulation of fat in the liver. This cause of this condition is still unknown. This disease can lead to scarring of the liver and eventually cirrhosis. Risk factors tend to include obesity, type 2 diabetes and high cholesterol.
- Prolonged alcohol abuse (chronic) – Chronic abuse of alcohol can lead to alcoholic liver disease due to the liver having to constantly process a number of toxins from the abuse of alcohol. This can result in scarring and over time, cirrhosis.