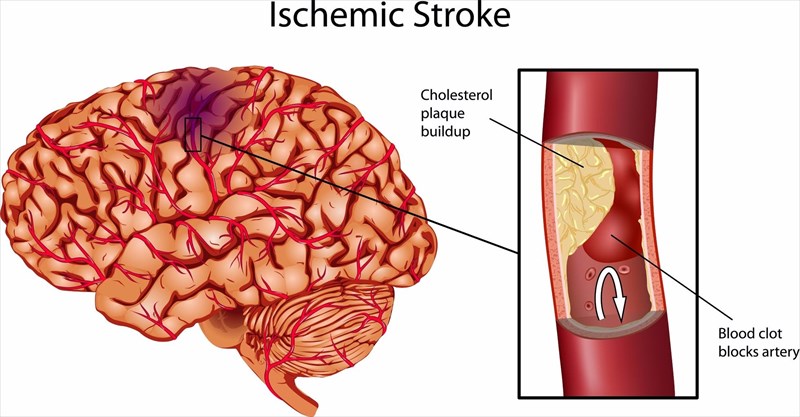
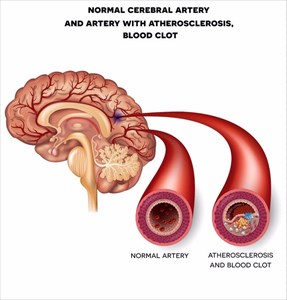
Blood flow may become sluggish and can sometimes result in clots having formed because of other health problems, such as an irregular heart rhythm (atrial fibrillation).
Haemorrhagic strokes are caused by bleeding in the brain as a result of aneurysms and ruptured arteries due to long-term damage, such as that from high blood pressure.
The most common risk factors of ischemic or haemorrhagic strokes include:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Type 2 diabetes
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Use of stimulant (or illicit) drugs, such as anabolic (muscle enhancing) steroids, cocaine and amphetamines
Other Articles of Interest

Obesity
Did you know that obesity raises the risk of having a stroke? Read more about this condition, it's causes and treatment here.
What does it mean if I have high blood pressure (hypertension)?
Having high blood pressure increases your risk of stroke and heart disease, however, a number of people with hypertension do not have any symptoms... Learn more here.
Diabetes (Diabetes Mellitus)
Having diabetes can also increase your risk of having a stroke. Learn more about this disease and how to get it under control here.
