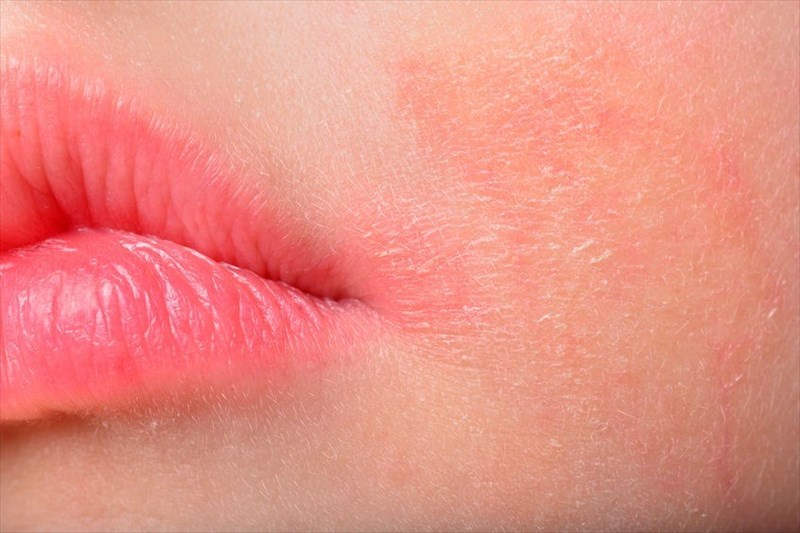
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- What are the symptoms and signs of eczema?
- What are the causes and risk factors for eczema (atopic dermatitis)?
- What are the different types of eczema?
- How is eczema (atopic dermatitis) diagnosed?
- How is eczema (atopic dermatitis) treated?
- Answers to frequently asked questions regarding atopic dermatitis
Causes of atopic dermatitis
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis and eczema, in general, is not yet known. The condition seems to have a link to a combination of environmental and genetic factors. In terms of atopic dermatitis, most sufferers have a basic skin (cutaneous) sensitivity, as well as an increased tendency toward itching and scratching. Atopic dermatitis has been seen to run in families, however, it is not yet known how the condition is passed from parents to their children.
Should a parent suffer from atopic dermatitis, hay fever or asthma, their child will have a higher chance of having at least one of these conditions. As a result, some experts suggest that the condition is linked to other atopic disorders such as asthma and hay fever (seasonal allergies), conditions that a number of individuals with atopic dermatitis also suffer from.
In addition to this, many children who have outgrown the symptoms associated with atopic dermatitis tend to develop asthma or hay fever later on. As such, researchers have termed this the 'atopic march', also referred to as the 'allergic march' which describes the transition from one type of allergic reaction to another over time. While one of these disorders doesn’t necessarily cause another, these conditions do, however, seem to be related, giving researchers some clues into further understanding atopic eczema (dermatitis) and allergies as a whole.
A number of people who are affected by eczema and atopic dermatitis tend to have either a defective form of the skin protein known as filaggrin or a decreased quantity of the protein (vital in retaining skin moisture) present in the body.
People with atopic dermatitis typically have a mildly compromised immune system. This predisposes them to developing infections and conditions such as eczema.
Although stress and environmental factors have been seen to aggravate eczema, these components have not been identified as underlying or primary causes for the condition.
Risk factors and triggers for atopic dermatitis
- Age – Being younger has been seen to be a risk factor for atopic dermatitis as infants and young children are most commonly affected by the condition with roughly 65% of cases occurring before the age of one and roughly 90% occurring before the age of five5.
- Harsh detergents and soaps – these irritate the skin and may cause flare-ups
- Low humidity – The lack of moisture in low humidity areas may trigger the skin to react adversely
- Over washing of skin and frequent hand washing – This can dry out and agitate the skin
- Sweating – The sodium found in perspiration can dehydrate the skin and lead to irritation.
- Staphylococcus bacteria – This type of bacteria causes skin infections
Common irritants for adults and children with atopic dermatitis
Substances that damage the skin when used for long enough in high concentrations may cause the skin to become inflamed, these substances are known as irritants. Detergents, soaps and perfumes can result in inflammation, as well as some cosmetic products. Alcoholic solvents, chlorine, sand and dust are also capable on aggravating atopic dermatitis.
The list below mentions some more common irritants:
- Synthetic fibres or wool
- Cosmetics, lotions and perfumes
- Detergents and soaps
- Sand or dust
- Cigarette smoke
- Dander or animal fur
- Pollen and flowers
- Chlorine, solvents or mineral oil
References:
5. University of Maryland Medical Centre. 2015. Eczema. Available: http://www.umm.edu/health/medical/altmed/condition/eczema [Accessed 06.10.2017]
