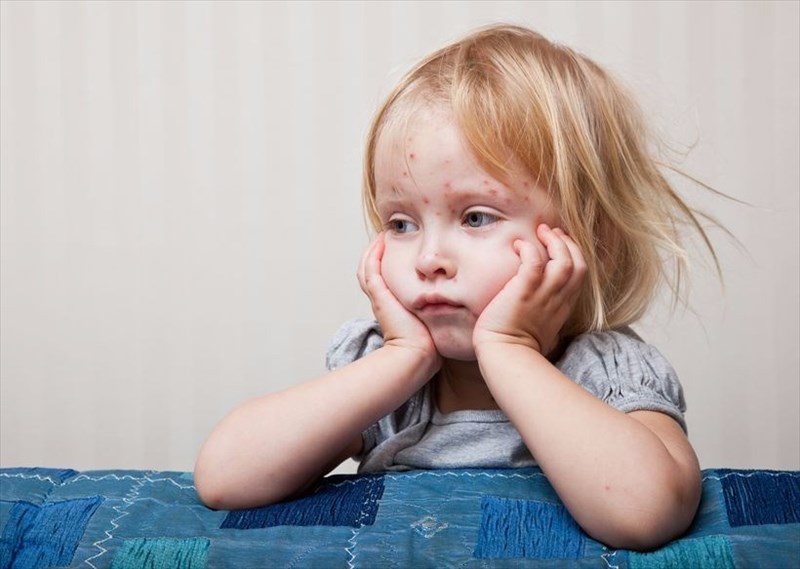

What is measles?
Measles, also known as rubeola, is a viral infection that affects the respiratory system, meaning that it inhabits the throat and nose of the infected person. It results in a rash all over the body as well as symptoms similar to those of the flu. These include a runny nose (congestion), a fever and a hacking cough (i.e. a short, dry, frequent cough). It is very easily transmitted through mucus of an infected person and can sometimes be fatal, particularly for children under the age of 5.
The virus is spread through sneezing, coughing and mucus contaminating surfaces, on which it can live for up to several hours once the mucus particles have settled.
Should you feel as though you may be at risk or have contracted measles, seek medical advice immediately so as to get professional diagnosis and treatment. It is important to note that the disease can easily be vaccinated against through the administration of the MMR vaccine.
If you have been in contact with an infected person and you have never been vaccinated, you will need to see your doctor for a vaccine within 72 hours of exposure. It is also possible to combat infection once exposed by taking a dose of immunoglobin (an immune system booster) within six days of exposure, this may prevent or lessen the symptoms of infection.
In the information found in the navigation menu above, we will take an in-depth look into the world of measles. Covering everything from the causes, symptoms and more. Please note that this article is intended to be used only as a guideline and not as a professional opinion. It is always best to consult with a doctor or health care professional for that.
Other Articles of Interest

German Measles (Rubella)
Rubella (also known as German measles) is a viral infection caused by the rubella virus. German measles is typically mild, but can be particularly serious for expectant moms. Learn more here...
Mumps
Mumps can be a painful condition that results in the swelling of the face. Learn all you need to know here...

Chickenpox (Varicella)
Falling ill with chickenpox can be a miserable experience, especially when red-filled blisters form on the skin and become itchy. Here's what you need to know about the condition...
