
PCOS affects a woman’s body in these three key ways:
- Excess androgen production: High levels of androgen hormones cause excess facial hair or abnormal hair growth on the body, as well as acne and androgenic alopecia (male-pattern baldness).
- Irregular or imbalanced menstrual cycles: Ovulation doesn’t happen in predictable patterns and menstrual cycles can be irregular (sometimes with intervals longer than 35 days, or with prolonged and heavy bleeding), infrequent (fewer than 8 periods in a year) or absent altogether for 4 consecutive months (or longer) – this is known as amenorrhoea.
- Polycystic ovaries: Enlarged and fluid-filled follicles or sacs on the ovaries.
Common signs and symptoms of PCOS
PCOS typically begins to show signs once a young woman begins to menstruate for the first time (during puberty when hormonal changes typically start). It is normal for a young girl / woman to experience irregular menstrual periods (heavy or irregular bleeding). The severity of this irregularity and other symptoms varies from one female to another. Other PCOS symptoms a young female will experience along with irregular menstrual cycles include:
A deeper voice
- Hirsutism - Excess hair on the face, as well as the chest area, stomach, toes and thumbs
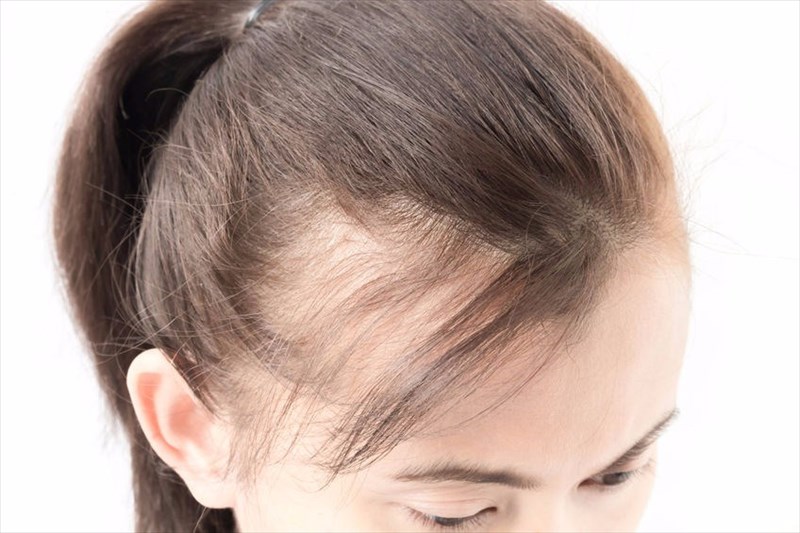
- Hair loss
- A small or decreased breast development size
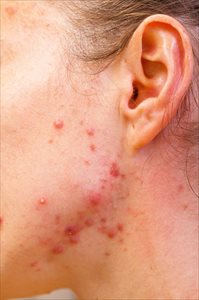
- Acne and oily skin
- Pain in the pelvic area
- Unexplained weight gain
- Depression and mood swings
- Infertility or repeat miscarriages
- Hyperinsulinemia (too much insulin in the body) or insulin resistance
- Skin tags
- Obstructive sleep apnoea (breathing problems during sleep)
It is not unusual for concurrent health concerns to develop along with excessive weight gain due to PCOS. These can include problems with hypertension, high cholesterol and diabetes. It is not advisable to take a wait-and-see approach when it comes to experiencing PCOS symptoms. Symptoms typically worsen with weight gain and an imbalance in levels of insulin in the body, causing complications. This is why it is important to seek medical attention for effective treatment, especially if you note excessive weight gain, abnormal hair growth or hair loss, severe acne and irregular menstrual cycles.
When should a woman seek immediate medical care for PCOS?
- If a woman experiences severe vaginal bleeding (bleeding is soaking through tampons or pads every hour for more than 2 hours)
- A woman has any signs of diabetes (frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, blurred vision, an unexplained increase in appetite, or a tingling / numbness in the feet and hands.)
- Increased mood swings or depression as a result of emotional problems related to physical symptoms, such as obesity and abnormal hair growth or hair loss.
Which doctors treat PCOS?
If a woman experiences any symptoms she may suspect to be related to PCOS, the following health professionals can all diagnose and treat the disorder:
- General practitioner (GP) or family physician
- Gynaecologist or obstetrician
- Internist
- Endocrinologist (including reproductive endocrinologists)
- Physician assistants and nurse practitioners

 A deeper voice
A deeper voice