- Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
- Precautions and considerations for taking Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
- How to use Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
- Side-effects of Atorvastatin (Lipitor) usage
- Discontinuation and withdrawal of Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
- The full treatment package – Atorvastatin, diet, physical activity & weight control
- What else should be taken into consideration regarding Atorvastatin (Lipitor)?
What is Atorvastatin (Lipitor) used for?
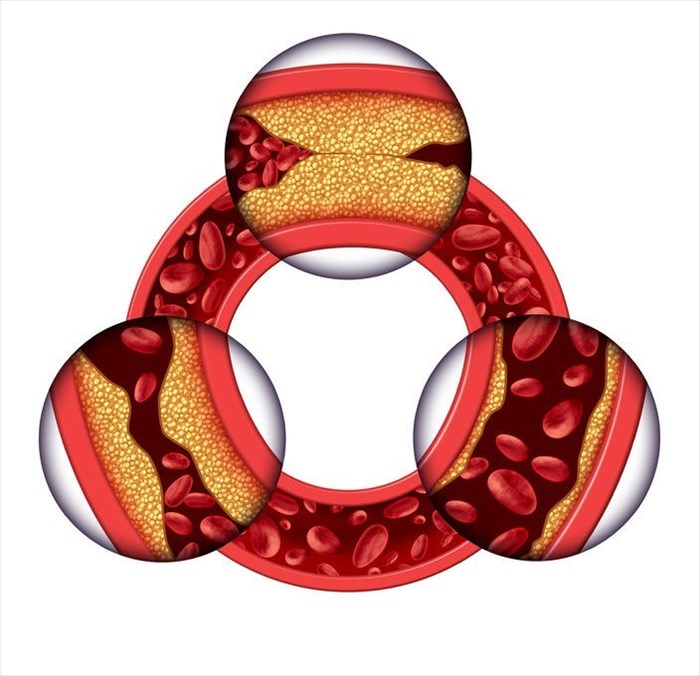
The medication works to lower cholesterol production (in the liver), and thereby reduce an accumulation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as the ‘bad cholesterol’ which can build-up along the linings of the body’s arteries walls (a condition known as atherosclerosis). Decreased accumulation of LDL cholesterol and fats thus reduces the risk of blood flow blockages which can result in severe medical conditions affecting numerous parts of the body, particularly the brain and the heart. As blood transports oxygen throughout the body, blockages which prohibit blood flow and as a result, oxygen supply, can result in severe health consequences that may quickly become life-threatening.
Atorvastatin / Lipitor is regarded as a clinically effective means to help prevent dire situations in relation to angina (chest pain), stroke, heart attack and heart (cardiovascular) disease. The chances of requiring heart surgery can also be considerably reduced.
How does Atorvastatin / Lipitor work with cholesterol in the body?
A waxy, fat-like substance, cholesterol can be found along the wall linings of cells throughout the body and circulates in the bloodstream too.
Not all cholesterol is bad for the body. The human body does require cholesterol in order to maintain overall good health. Cholesterol is used by the body to help build cells, and produce hormones, vitamin D, bile acids and various other necessary substances. Generally, the body produces and uses as much cholesterol as it needs for optimum function. Being a fatty / waxy substance, it is able to circulate in the bloodstream by means of lipoproteins (a combination of lipids and proteins that carry fats in the body).
Excess cholesterol production shifts the balance between healthy and useful amounts and trouble, and thus begins to influence the body badly. Cholesterol is produced in the liver and is both metabolised and removed from the body via the organ. It can be found in a variety of foods too.
Triglycerides are another fat-like substance that are obtained from food and also produced in the liver, they too circulate in the bloodstream. Excessive levels of these in the body are also preventable as they are largely elevated by unhealthy habit factors such as excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, obesity and a high carbohydrate diet.
When both of these fatty substances occur in excess within the body, build-up are formed (these are referred to as plaque) and blockages may occur as the arteries become clogged. Blood vessels begin to narrow (constrict) and become less flexible. Oxygen and nutrients are also hindered from circulating within the body and reaching tissues requiring these substances for optimum function. This can lead to a condition known as atherosclerosis (‘a hardening of the arteries’). High cholesterol levels become problematic in those who smoke, have high blood pressure (hypertension), are prone to developing heart disease or have diabetes.
Atorvastatin / Lipitor works to reduce the accumulation of excess fatty substances in the bloodstream – low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL / ‘bad cholesterol’) and triglycerides. The medication also works to increase the amount of healthy cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol / HDL). As a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, Atorvastatin / Lipitor hinders cholesterol biosynthesis, thus lowering accumulation risk (i.e. it blocks the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme in the liver and aids in the breakdown of lipids in the bloodstream).
Atorvastatin / Lipitor ingredients
During consultation, a doctor will take into consideration the ingredients of this medication. This is necessary in the event that a patient has a known allergy or sensitivity to a particular ingredient, which could result in an adverse reaction once treatment commences.
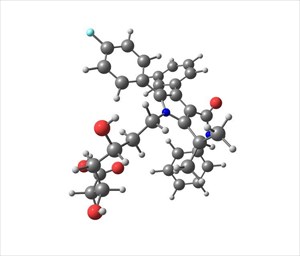
The active ingredient in this medication is Atorvastatin calcium (at strengths of 10mg, 20mg, 40mg and 80mg). Inactive ingredients include:
- Candelilla wax
- Calcium carbonate
- Hydroxypropyl cellulose
- Croscarmellose sodium
- Microcrystalline cellulose
- Lactose monohydrate
- Polysorbate 80
- Opadry White YS-1-7040 (talc, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide)
- Magnesium stearate
- Simethicone emulsion
Overview of the metabolism mechanics of Atorvastatin
- Absorption: Once swallowed, the medication is absorbed within 1 to 2 hours, achieving maximum plasma concentrations. Absorption rates are proportional to the dosages given to a patient.
- Distribution: The active ingredient, atorvastatin calcium, binds to the majority of plasma proteins (approximately 98%) and has a mean distribution volume of about 381 litres.
- Metabolism: The medication is metabolised mostly by the cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) enzyme that mainly exists in the liver and intestine. Metabolism also involves ortho- and parahydroxylated metabolites, and beta-oxidation products.
- Excretion: The medication is mostly removed from the body via bile once metabolised within 14 hours. Less than 2% of the medication may be removed via urine.
Atorvastatin / Lipitor usage
Adult use
Common conditions associated with LDL cholesterol (‘bad cholesterol’) which can be effectively treated with this medication include:
- Hyperlipidemia (high amounts of fatty substances / lipids in the bloodstream)
- Hypertriglyceridemia (high amounts of triglycerides in the bloodstream)
- Primary dysbetalipoproteinemia (high LDL-cholesterol levels and low HDL-cholesterol)
- Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (an inherited genetic condition whereby the body is incapable of naturally managing cholesterol levels or removing ‘bad cholesterol’, resulting in high LDL-cholesterol / excess ‘bad cholesterol’)
- Prevention of cardiovascular disease and related conditions, as well as stroke.
Paediatric use (10 years of age and up)
Excess fatty substances (‘LDL-cholesterol’) can affect children too. Atorvastatin / Lipitor is also safe for prescription recommendation for children between the ages of 10 and 17, showing no significant adverse effects on normal growth development, sexual maturation or female menstrual cycles. (1)
The medication can be effective for treatment purposes and is also tolerated well. It has not yet been conclusively established as safe for use in children younger than 10 years of age and is thus not generally approved for use.
The most common condition affecting children (and adolescents) who require this medication is homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. The medication helps to better manage cholesterol and remove that which is not beneficial for health from the body. Those with this condition appear to tolerate Atorvastatin / Lipitor better (with improved treatment targets) than other lipid-lowering medications.
Atorvastatin combination products
The medication is also available as a combination product, containing other treatment ingredients. Those available include:
- Caduet® (contains Atorvastatin and Amlodipine) – a combination of a calcium channel blocker and a statin used in the treatment of high cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Liptruzet® (contains Atorvastatin and Ezetimibe) – a combination cholesterol blocker and statin used in the treatment of high cholesterol.
Reference:
1. US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health. September 2016. A 3-year study of atorvastatin in children and adolescents with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27678432 [Accessed 05.02.2018]
Other Articles of Interest
Liver Disease / Hepatic Disease
The liver is a phenomenal organ with the ability to heal itself. However, in some cases, the constant damage and abuse to it can cause liver disease and even liver failure.
Diabetes (Diabetes Mellitus)
Diabetes (diabetes mellitus) is a long-term disease that requires daily management and care. The illness refer to a group of metabolic health conditions that affect how the body functions...

Thyroid Disorders
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland that functions as an important regulator in the endocrine system. We take a look at the most common malfunctions that cause thyroid disorders...