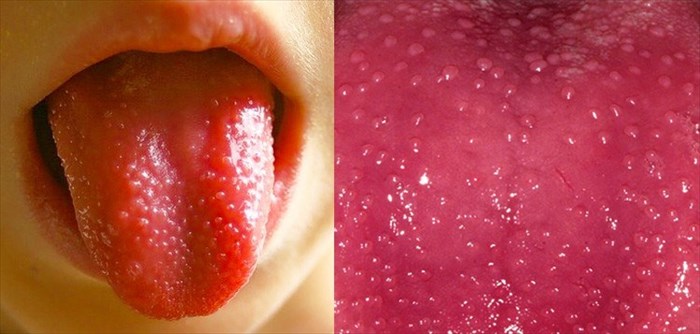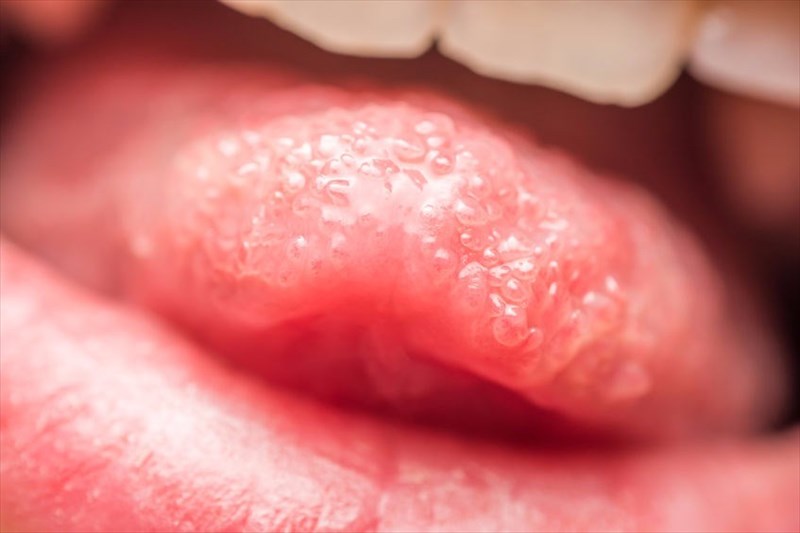
What is strawberry tongue?
The term ‘strawberry tongue’ describes a tongue that is bumpy and swollen, in a number of cases the tongue is also red and enlarged, resembling a strawberry or even a raspberry. Therefore, the term itself is rather self-explanatory. Occasionally, the tongue may be white over a few days, after which it will turn red.
Strawberry tongue is not a condition in itself but rather a symptom that is a result of another disorder or condition.
The diagnosis and treatment will depend on the underlying condition, and once treatment has commenced, the tongue will typically return to its original colour. A healthy tongue is pink and covered in small nodules known as papillae. In the case of a strawberry tongue, the tongue’s light pink colouring on these nodules will deepen and become noticeably red and inflamed.
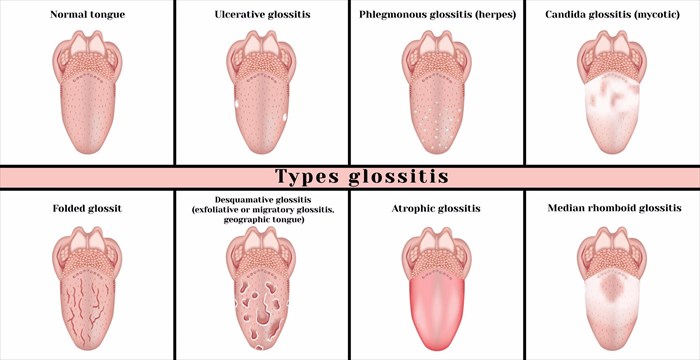
The differentiating factor between strawberry tongue and other conditions of the tongue, such as glossitis, is that strawberry tongue results in prominent red bumps on the tongue, whereas glossitis refers to the red colouring and inflammation of the tongue, but is not characterised by bumps. Glossitis will be discussed further below.
What are the causes of strawberry tongue?
There are a number of different causes that can result in a bumpy and swollen tongue. Your doctor will typically ask you about the associated symptoms and conduct a physical examination to determine the underlying cause of an inflamed tongue.
The following are conditions that can cause strawberry tongue as a symptom:
Scarlet fever
This bacterial condition commonly occurs when strep throat is left untreated. Scarlet fever results in a red rash that covers a large part of the body and is typically seen in children between the ages of five and fifteen. Scarlet fever is normally a short-term illness and will resolve within a number of days or weeks with the aid of a professional diagnosis and a course of antibiotics.
The symptoms of scarlet fever include:
- White strawberry tongue in the first few days which will eventually turn red afterwards
- Red rash covering a large portion of the body
- High fever
- Sore throat
- Headache
- Red lines forming in the folds of the skin (particularly around the groin)
Allergies
Drug or food allergies can result in a number of symptoms, strawberry tongue being one of them. An allergic reaction occurs when the immune system attacks something that is mistakenly recognised as a threat. The body releases a chemical known as histamine that causes a number of the symptoms associated with allergies.
The consumption of certain fruits and vegetables is a common culprit in the development of strawberry tongue as part of an allergic reaction. The common treatment for allergic reactions is antihistamines, or in more severe cases, an EpiPen will be used if the throat closes up from inflammation and the airways are blocked.
The symptoms of allergies include:
- Watery and itchy eyes
- Scratchy mouth and throat
- Rash
- Difficulty breathing (this is may lead to anaphylactic shock and is a medical emergency)
- Strawberry tongue
Vitamin deficiency
A deficiency of the vitamin B-12 can also result in strawberry tongue. Vitamin B-12 plays a key role in the functioning of the nervous system and brain, as well as the formation of the red blood cells in the body. If the B-12 levels are low, then the red blood cell count will deplete and may result in anaemia. Anaemia is a condition where there are not enough red blood cells present in the body.
The symptoms of a B-12 deficiency include:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Memory issues (cognitive)
- Balance difficulties
The symptoms of anaemia include:
- Dizziness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Skin pallor (pale skin)
- Light-headedness
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
Kawasaki disease
Kawasaki disease is a rare condition that is commonly seen in children, however, it can develop in adults too. It is not yet clear as to why some people develop Kawasaki disease and others do not, therefore the risk factors are not certain.
The disease results in inflammation occurring in some of the body’s arteries. The condition is usually treatable with the initial treatment therapy including intravenous immunoglobin and aspirin. The intravenous medication will be administered in a medical facility.
The symptoms Kawasaki disease include:
- Rash
- High fever
- Irritated and red eyes with thick discharge in some cases
- Peeling and flaking skin
- Inflammation in feet and hands
- Chapped lips
- Strawberry tongue
Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
Toxic shock syndrome is a rare and life-threatening reaction or side effect of some bacterial infections. The condition occurs suddenly and is caused by the release of certain toxic and harmful substances due to a bacterial overgrowth known as staph or Staphylococcus aureus.
This bacterium is found in a number of women’s bodies and TSS often affects women who are menstruating and is associated with the incorrect use of tampons. However, men are also able to develop the condition if they have been exposed to this specific strain of staph bacteria from recent surgery, open wounds, or if they are using a prosthetic device. The body reacts to the bacteria through a rapid drop in blood pressure leading to the organs being deprived of oxygen which can result in death.
Some of the risk factors include open wounds, the use of tampons that are super absorbent without changing them regularly, and recent surgery. Nasal packing which involves the application of gauze, cotton wool or sterile tampons to the nasal chamber in order to apply continuous pressure to the nasal septum in an attempt to stop bleeding, has also been identified as an associated risk factor.
The symptoms of toxic shock syndrome (TSS) include:
- High fever that suddenly develops
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea or vomiting
- The development of a rash that looks like a sunburn on soles of feet and palms of hands
- Headache
- Confusion
- Muscle aches and pains
- Strawberry tongue
It is vital to know that TSS can be a fatal condition and requires immediate medical attention and should be treated as a medical emergency.
Strawberry tongue and glossitis
Glossitis is a term that describes the tongue being inflamed. Glossitis causes swelling of the tongue, the tongue will also change colour and appear smooth on the surface, making the small nodules on the tongue (papillae) disappear. These papillae play a vital role in how we eat food and contain hundreds of thousands of small sensors known as taste buds.
The vital difference between glossitis and strawberry tongue is that the latter results in visible raised bumps on the tongue and glossitis results in the tongue swelling, changing colour and developing a smooth surface.
Glossitis, much like strawberry tongue, is often a symptom of an illnesses or health condition and not a condition on its own. However, it generally occurs as a result of an underlying condition that does not have any relation to those causing strawberry tongue.
The most common conditions that cause glossitis include:
- Anaemia (iron-deficiency and pernicious forms)
- Deficiencies in vitamin B complex
- Untreated coeliac/celiac disease
- Xerostomia (dry mouth)
- Allergic reactions
- Infections of the mouth caused by bacteria, viruses or yeast
- Hormonal imbalances
- Injury to the tongue caused by burns, ill-fitting dentures or rough teeth
Symptoms of glossitis include:
- A red, inflamed tongue that has a smooth surface (no papillae are evident)
- A sore tongue
- Swelling of the tongue (which when severe may block the airway, although this is rare)
- Difficulty in speaking, chewing or swallowing due to discomfort and pain
Generally, glossitis resolves on its own once the underlying cause has been treated.
Other Articles of Interest

Anaemia
Did you know that there are over 400 variations of anaemia? We define the condition, its causes, symptoms and how to go about effectively treating it.

Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS)
A sudden high fever and a sharp drop in blood pressure are some of the main warning signs for toxic shock syndrome. Learn more about how to recognise this potentially life-threatening condition here.

Kawasaki Disease
Kawasaki disease is seen mostly amongst children and typically involves a high fever, swollen lymph nodes and a rash. Find out if your child has the condition...