- Thyroid Disorders
- Common types and underlying causes of thyroid disorders
- Signs and symptoms of thyroid dysfunction
- What risk factors are associated with thyroid disorder?
- Diagnosing thyroid disorders
- Treatment for thyroid disorders
- Common complications of thyroid disorders
- Outlook for thyroid disorders
What happens to the body when the thyroid malfunctions?
Symptoms of thyroid dysfunction are as varied as the underlying causes. These are as follows:
Hyperthyroidism symptoms
Common sign and symptoms of an overactive thryoid include:
- Rapid heart rate (racing heart or an irregular heartbeat) and palpitations
- Nervousness
- Restlessness
- Anxiety
- Agitation / irritability
- Profuse sweating
- Heat intolerance
- Thinning skin
- Clammy skin
- Brittle hair and nails
- Muscle weakness
- Joint pain
- Unintentional weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Sleep issues (insomnia)
- Shaking (hand tremor)
- Problems with concentration (mental fog)
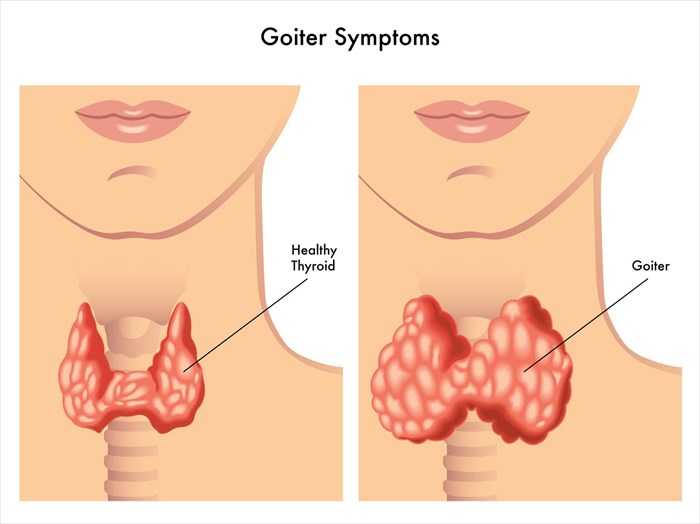
- Enlarged thyroid (goitre)
- Frequent bowel movements or diarrhoea
- Vision disturbances and enlarged or bulging eyes (Grave’s disease).
Women may also experience reduced and irregular menstrual cycles (reduced or ceased flow). Children may experience behavioural problems and hyperkinesis (hyperactivity and the need to constantly move around) over and above other symptoms. Seniors are also more likely to experience angina (chest pain if prone to heart disease), shortness of breath (if prone to heart failure), and osteoporosis.
Hypothyroidism symptoms
Common sign and symptoms of an underactive thryoid include:
- Unintentional weight gain
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to cold temperatures
- Dry skin
- Dry and thinning hair
- Puffiness around the eyes
- Slow heart rate
- Body weakness
- Muscle and joint aches
- Problems with memory function
- Concentration problems (mental fog)
- Constipation
- Poor appetite
- Fluid retention (bloating)
- High cholesterol levels
- Enlarged thyroid (goiter/goitre)
- Hoarse voice
- Depression
Women may also experience excessive or prolonged menstrual bleeding during periods (or heavy and irregular menstruation). Signs in infants include poor feeding, poor growth rate, constipation, excessive sleeping, and jaundice (yellowing of the whites of the eyes and skin). Young children will experience similar symptoms to those of adults, along with poor growth, delayed sexual maturation and tooth development.
Goitre / thyroid nodules (moderate to severe enlargement)
The symptoms of a goitre / thyroid nodules include:
- Swelling in the neck
- Feeling of tightness in the neck (pressure on the oesophagus and trachea)
- Small dry cough (or wheezing)
- Hoarse voice
- Pain and diifficulty with swallowing or breathing (due to pressure on the oesophagus and trachea). Pressure sensations may worsen when the head is tilted forwards (down).
Thyroid cancer
Warning signs include:
- A noticeable lump or swelling in the neck
- Difficulties with swallowing and breathing
- Constant wheezing
- Pain in the neck (sometimes spreading to the ears)
- Coughing
- Hoarse voice
When to call the doctor if you suspect that you have a thyroid problem
Signs of an overactive or underactive thyroid generally develop slowly, anywhere between a handful of weeks to a few months. All problems with the thyroid must be assessed by a medical doctor and effectively treated.
Hypothyroidism, for instance, left untreated can have serious effects on the functioning of the brain, as well as lead to intestinal obstructions and dysfunction of the heart (inability to beat effectively). Complications may also arise if exposed to infection, cold temperatures, certain medications and even trauma, leading to worsened symptoms.
Severe hyperthyroidism is also known as ‘thyroid storm’ or thyrotoxic crisis. This condition is potentially life-threatening and can also have severe complication effects on both the heart and brain.
Signs and symptoms of all thyroid problems are fairly similar to a variety of other medical conditions, making it difficult to diagnose without testing. Any signs that include abdominal pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, extreme neck pain, sudden enlargement of the thyroid gland (lump in the throat), difficulty swallowing, confusion and disorientation, dizziness, high fever, vomiting or even coma must be treated as a medical emergency.