What causes blue fingernails?
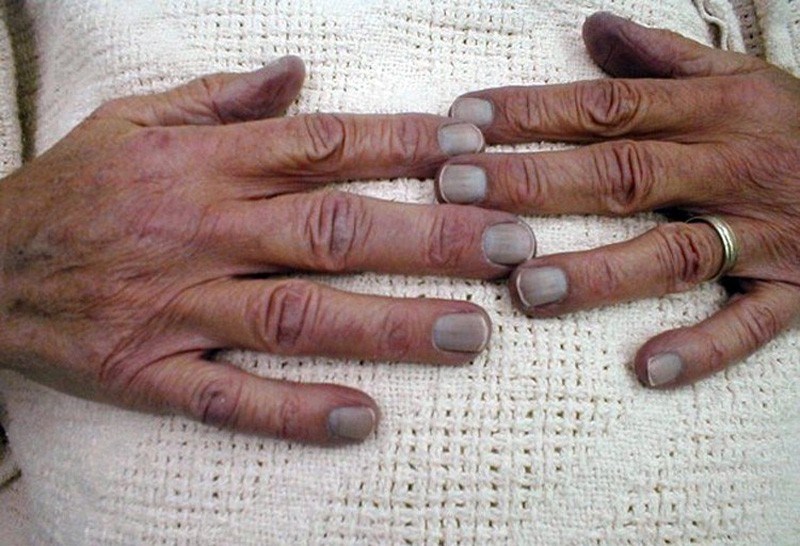
The correct medical term for a bluish colour or hue of the skin, including the skin that is underneath the fingernails, is cyanosis. Blue fingernails are a symptom of this condition.
**My Med Memo - Cyanosis occurs as a result of poor circulation or an inadequate amount of oxygen present in the blood.
Medically speaking, blue fingernails are caused by hypoxaemia, an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. This low level of oxygen in the blood results in the skin or the membrane beneath the skin turning a bluish colour (or sometimes even purple).
This skin discolouration may also suggest that there is a high amount of an unusual form of haemoglobin found in the blood that is circulating in your body. Haemoglobin is a protein molecule found in the red blood cells that contains oxygen which it carries from the lungs to the various tissues in the body, it then returns with the carbon dioxide it collected from these tissues back to the lungs. Simply put, haemoglobin is tasked with the job of transporting oxygen in the blood.
There are a number of factors and underlying health conditions that can cause fingernails to turn blue. These are discussed below.
Cold temperatures
It is possible for cold temperatures to make the fingernails appear blue, bear in mind it is the skin underneath the nails, the nail bed, that turns blue and not the actual nail itself. When nails appear blue from cold temperatures it is due to the cold restricting your blood vessels and forcing them to narrow. This creates narrow pathways which make it hard for an adequate amount of blood that is oxygen-rich to reach the skin beneath the nails. Therefore, if you are cold, this can temporarily slow the flow of blood through the skin.
If normal nail colour returns once the hands are warmed or massaged, then the bluish appearance is likely to be due to the cold temperatures. When fingernails turn blue from the cold, this is a normal physiological reaction as the body begins to shift blood flow from the limbs, hand and feet, to the chest and abdomen so that internal body temperatures are maintained and the organs can remain a healthy temperature.
If the fingernails remain blue even when you warm up then an underlying condition may be interfering with the body’s ability to carry oxygenated red blood cells to the various organs and tissues. Let's examine these now:
What conditions can cause blue fingernails?
Blue fingernails may be caused by an underling health condition that results in blue fingernails as a symptom, and in some cases, the blue skin discolouration becomes a chronic condition.
The various common causes of cyanosis are explained below, however, you should never diagnose yourself and should always seek the professional opinion of a doctor if you notice a change in the colour or texture of your nails.
Causes of cyanosis that affect the feet, limbs or hands
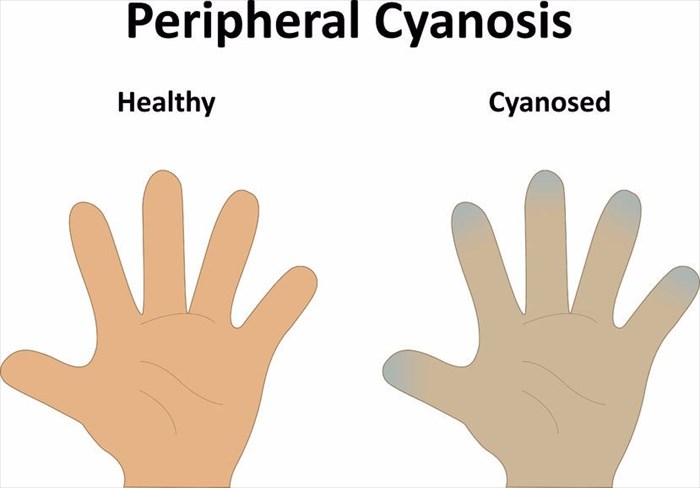
If just the toes, limbs or fingers are blue, this is referred to as peripheral cyanosis. These body parts may also feel cold as the cause of the cyanosis is typically from poor circulation as a result of:
- Raynaud's phenomenon (also known as Raynaud syndrome) – This is a condition where the supply of blood to specific parts of the body, particularly the fingers and toes, is temporarily reduced as a result of exposure to cold weather (temperatures). In people with this condition, the arteries constrict as a response to the cold and thus limit the supply of blood to the area that is affected. The fingers or toes will feel numb and turn blue as a result.
- PAD (peripheral arterial disease) – This is a disease where a build-up of plaque (fatty deposits) accumulates in the arteries responsible for transporting blood to the organs, limbs and head. Thus, the blood supply is restricted to the limbs.
- Blood clots – Blood clots form as a result of the blood components known as platelets and plasma proteins, thickening, this forms a mass that is semi-solid. This reaction can be triggered by injury or can occur accidentally inside of your blood vessels without any damage being done to the vessels. When these clots have formed, they are able to move to different parts in the body and can cause damage and block the supply of blood to a limb, or even from a limb.
- Beta-blocker use – These medications, like Metoprolol sold under the brand names Lopressor or Toprol XL, are used in the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure). These drugs slow down the heart rate and can result in the blood flow to the limbs decreasing.
Causes of cyanosis that affect the lips and/or skin in general
If all or most of the skin and/or lips appear to have a bluish hue to them, this is referred to as central cyanosis. This form of cyanosis is normally a sign of the oxygen levels in the blood being low. The causes of central cyanosis are explained below:
Disorders of the lungs
The lungs and respiratory system allow for oxygen to be taken from the air that is breathed in, the lungs also rid the body of carbon dioxide when it is breathed out. The lungs are tasked with the important job of ensuring that oxygen is transported throughout the body in order for it to function. If their functional ability is impaired in some way, this can result in the blood containing less oxygen resulting in cyanosis. This may occur due to:
- The worsening of a current chronic lung disorder - When a chronic lung condition such as COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) or asthma worsens, the body can be deprived of sufficient oxygen to function. COPD is a condition that involves the airflow being blocked, this makes it difficult to breathe. Asthma refers to a condition in which the airways are narrow and inflamed, this also blocks airflow and thus the levels of oxygen are depleted in these two conditions.
- Lung infections – Some infections that restrict oxygen intake include whooping cough, bronchiolitis and pneumonia. Bronchiolitis commonly seen in infants and children and is a condition wherein their small air passages become infected.
- Pulmonary embolism – This refers to a blood clot forming in the arteries of the lungs.
- Bronchiectasis – This is a condition in which the airways in the lungs become damaged, thickened and widened as a result of a bacterial infection. This infection makes it difficult for mucus to be cleared.
- ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome) or NRDS (neonatal respiratory distress syndrome) – These are conditions wherein the lungs are unable to provide an adequate amount of oxygen to the rest of the body. These disorders involve fluid collecting in lung’s air sacs, thus, depriving the organs in the body of oxygen.
- Nearly drowning or drowning – When drowning, water will fill up in the lungs, thus cutting off the oxygen supply to various body parts.
Disorders of the airways
- Croup – This is a condition seen in children and is normally a result of a virus. Croup affects the child’s airways and results in a cough known as a barking cough.
- Anaphylaxis – This condition refers to a severe allergic reaction resulting in the constriction of the airways.
- Epiglottitis – This is a disorder in which the tissue flap located at the back of the throat becomes swollen and inflamed as a result of an infection.
- Choking – This will occur when a piece of food or an object is lodged in your windpipe or throat, thus blocking the air flow.
Disorders of the heart
- CHD (congenital heart disease) – This condition refers to an abnormality that occurs before birth and can affect how blood travels through the body and heart.
- Heart failure – This refers to a condition wherein the heart stops pumping enough blood for the body to function.
- Cardiac arrest – This is a condition wherein the heart will stop beating.
Other causes of cyanosis:
- Being exposed to cold water or cold air (Frostbite occurs when the limbs or body parts have been exposed to the cold for too long and involves the skin and the tissue found just below the skin, freezing)
- Being at a high altitude where the level of oxygen in the air is low
- Having an issue with the blood such as polycythaemia or abnormal haemoglobin. Polycythaemia refers to a high amount red blood cells being present. Abnormal haemoglobin refers to the blood not being able to absorb enough oxygen due to abnormal haemoglobin proteins.
- Having a seizure over an extended period of time.
How is cyanosis diagnosed and treated?
In order for cyanosis for to be diagnosed, a doctor will need to measure how much oxygen is present in the blood, this is done through testing with a non-invasive pulse oximeter. This is a medical device that will indirectly monitor the presence of oxygen (oxygen saturation) in the blood. The process of using this device will involve placing a cup-like instrument on a body part, such as an ear lobe or finger. This probe will use light in order to measure the level of oxygen in the blood.
ABGs (arterial blood gases) are also conducted. This test will measure the pH (acidity), carbon dioxide and oxygen present in the blood through a sample taken from an artery. An ABG will determine the ability of the lungs to move oxygen into the blood and remove any carbon dioxide from it.
The treatment for cyanosis will normally depend on the underlying cause identified by your doctor. He or she will also work towards restoring an adequate amount of oxygen to the blood.
When is cyanosis a medical emergency?
Those with blue fingernails should be aware of the following symptoms that may develop along with, or shortly after blue fingernails become evident. These are considered a medical emergency:
- Having difficulty breathing
- Profusely sweating (without physical exertion)
- Experiencing chest pain (angina)
- Having numbness or pain that does not resolve (this is experienced in the hands, fingers or arms)
- Fainting or feeling dizzy
Other Articles of Interest

Croup
Swelling in the vocal cords, voice box, bronchial tubes and windpipe is often as a result of croup. Here, we define the causes and types of croup, as well as how to recognise the signs...

What to do when someone is choking
Choking is a life-threatening medical emergency with mere minutes to appropriately respond to. Knowing what to do correctly can save someone's life. We give you a comprehensive breakdown here...

Frostbite
A serious medical condition, frostbite can lead to severe and irreversible tissue damage. A common freezing injury, we breakdown what happens, what causes it and how best to go about treating it...