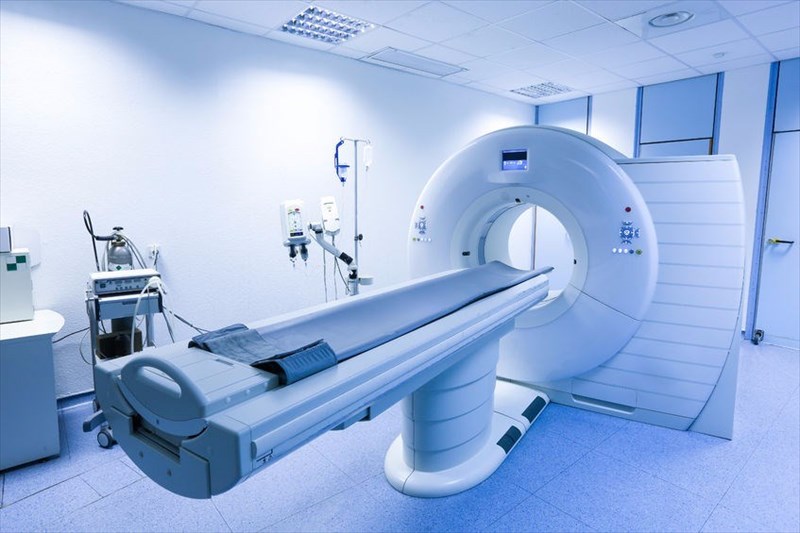
What is a CT scan?
A CT scan, or computerised tomography, is a means of medical testing that combines a series of X-ray images and computer processing to create cross-sectional visuals of the inside of the body. X-ray images are taken at a variety of different angles that provide a detailed view of bones, organs, soft tissues and blood vessels.
This means of testing is a highly accurate way for medical professionals to quickly examine a person who may have serious internal injury or bodily trauma. A doctor can see just about the entire body using the technology of this visual imaging test. The highly-detailed images created provide much needed visual information that enables a medical doctor to accurately diagnose a problem, disease, injury or abnormality. In turn, the most effective means of treatment can be implemented, lowering the risk of further damage.
 Key areas of the body a doctor may recommend a scan to gain a better perspective of include:
Key areas of the body a doctor may recommend a scan to gain a better perspective of include:
- The head
- The spine
- The shoulders
- The chest
- The heart
- The abdomen
- The knees
The series of images taken during the testing procedure are combined using computerised software that creates cross-sections or slices to form detailed images of the inside of the body. Here, any abnormalities will be clearly shown and easily diagnosed. A 3-D image can be created of a particular area of the body for medical professionals to gain a clearer idea as to what may be malfunctioning or damaged, and make a more accurate diagnosis.
A CT scan is minimally invasive and is a completely painless experience. It can also be done relatively quickly, which can be very useful in time-sensitive medical situations.
Other Articles of Interest
Spinal stenosis
What is spinal stenosis? We take a look at the structure of the spine and how abnormal narrowing and constriction affects the ability to move, turn and twist...
Cancer
Cancer is an umbrella term for a group of diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. Read this overview article to find out all you need to know about the progressive disease.

Blood clot
What are blood clots and how do they occur? Learn more about when the formation of a blood clot becomes a little more serious and what to do about it here...

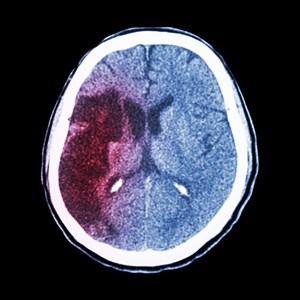 Key areas of the body a doctor may recommend a scan to gain a better perspective of include:
Key areas of the body a doctor may recommend a scan to gain a better perspective of include: